#Immune checkpoint inhibitors
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Understanding Immunotherapy for Autoimmune Diseases
Introduction
Immunotherapy, a groundbreaking approach primarily recognized for cancer therapy immunotherapy, is now making significant strides in treating autoimmune diseases. This article delves into how immunotherapy is applied beyond cancer immunology immunotherapy to manage and treat autoimmune conditions.
The Mechanism of Immunotherapy in Autoimmune Diseases
Immunotherapy works by modulating the immune system, enhancing its ability to fight diseases. Unlike in immunotherapy cancer treatment, where the goal is to target and destroy cancer cells, in autoimmune diseases, the therapy aims to recalibrate the immune system to stop attacking the body's tissues.
Types of Immunotherapy for Autoimmune Diseases
There are various types of immunotherapy used to treat autoimmune diseases. These include monoclonal antibodies, cytokine inhibitors, and immune checkpoint inhibitors, each designed to alter specific immune system pathways. While some of these therapies overlap with those used in cancer treatment, their application in autoimmune diseases focuses on immune regulation and suppression of overactive immune responses.
Immunotherapy Medications and Treatments
Immunotherapy medications for autoimmune diseases are tailored to reduce inflammation and curb the immune system's erroneous attacks on healthy cells. The precise medication or combination of therapies depends on the specific autoimmune condition being treated, highlighting the personalized nature of immunotherapy.
The Role of Immunotherapy and Vaccines
Exploring the intersection of immunotherapy and vaccines reveals potential for preventative strategies in autoimmune diseases. Vaccines designed to induce tolerance in the immune system are under research, potentially preventing autoimmune diseases from developing or worsening.
Managing Side Effects and Costs
While immunotherapy offers new hope, it's crucial to consider immunotherapy side effects and immunotherapy cost. Side effects vary widely, from mild to severe, and must be carefully managed under medical supervision. The cost can also be significant, necessitating a discussion about healthcare resources and insurance coverage.
Conclusion
Immunotherapy for autoimmune diseases represents a promising frontier in medical treatment, offering hope for millions suffering from these conditions. As research progresses, it could redefine the therapeutic landscape for autoimmune diseases, much like it has for cancer.
Discovering Excellence in Cancer and Autoimmune Disease Treatment at CBCC India
At the forefront of medical innovation and care, CBCC India stands as one of the leading Cancer Hospital in India, dedicated to eliminating cancer and advancing treatment for autoimmune diseases. Our commitment to innovative research and exceptional care ensures that every patient receives personalized, state-of-the-art treatment. Discover the pinnacle of healthcare excellence at CBCC India, where we strive to conquer cancer and improve the lives of those with autoimmune diseases through cutting-edge immunotherapy and comprehensive care.
#Immunotherapy#Autoimmune diseases#Cancer therapy#Immune system modulation#Monoclonal antibodies#Immune checkpoint inhibitors#Inflammation reduction#Personalized treatment#Vaccines
1 note
·
View note
Text
youtube
#LRRC25#gastric cancer#biomarker#immunotherapy#immune response#tumor microenvironment#immune checkpoint inhibitors#precision medicine#oncology#cancer research#personalized treatment#cancer prognosis#tumor immunity#targeted therapy#cancer biomarkers#molecular oncology#immune regulation#clinical oncology#cancer survival#predictive marker.#Youtube
0 notes
Text
#CTLA-4 Therapies Market#Global Market Trends#Latest Therapeutic Advancements#Innovations in CTLA-4 Therapies#Recent Developments in Immunotherapy#Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors#Cancer Treatment Breakthroughs
0 notes
Text
https://social.studentb.eu/read-blog/178693_immune-checkpoint-inhibitors-market-size-overview-share-and-forecast-2031.html
The Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market in 2023 is US$ 47.22 billion, and is expected to reach US$ 158.26 billion by 2031 at a CAGR of 16.32%.
#Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market#Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market Trends#Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market Growth
0 notes
Text
The Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 17% during the forecast period, i.e., 2022-27. The growth of the market would be driven primarily by the rapidly increasing incidence of cancer worldwide & the mounting demand for effective & safe treatments, i.e., instigating governments to enhance the healthcare infrastructure to cater to the high unmet patient needs.
#Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market#Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market News#Global Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market Growth
0 notes
Text
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market
#Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market scope#Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market report#Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market research
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text

Food for Thought - Chapter 1
Summary: You often wonder why you feel so alone even when you spend time with other people. An outsider even in a packed room. But a chance work project with Urahara Kisuke provides a strange comfort... so strange that you continue to spend time with him after your project is over.
Content warning: Reader is written with self-esteem issues/insecure thoughts, food is a large part of this story. Kisuke will become a yandere in this, he is also promiscuous. This chapter has no smut, but it will become very NSFW soon.
Read on AO3 here.
Chapter 1: Blini with caviar and crème fraiche
“You’re still up for karaoke tonight, right?” Your co-worker Hanatarou asked, as he peered over your cubicle.
You smiled brightly at him, eyes filled with mirth, “of course! I don’t back down from a challenge, especially one from Madarame” you snickered. Hanatarou laughed as he thanked you again for agreeing to come with him to a singing showdown. You knew Hanatarou since you started working at the Senjumaru & Hikifune Diagnostics Company. While you and Hanatarou were new in your roles, you sensed that there was an ongoing rivalry between your department and Madarame Ikkaku’s - the marketing team.
But before you could figure out your song list for the night, your manager, Sarugaki Hiyori shouted for you, “Oi! C’mere quick. I got a new project for you, newbie.”
It had been over two years since you started your job here, but you couldn’t help but laugh at Sarugaki still calling you “newbie”, but the casual behaviour you two shared was something you appreciated in your role.
“I got a new project for you.” Hiyori explained, walking you towards the meeting room. “The higher ups were impressed with how you dealt with the immune checkpoint inhibitors assessment.”
“Thank you, but it was a team effort after all.” You explained, which was true to a degree, but you were the lead analyst on the project.
“Don’t be so modest,” Hiyori scoffed, “anyways they want you to do a review on the prefecture’s medical imaging inventory.”
“I see, but that’s not my area of expertise, wouldn’t Akon or Nemu be better fits?” You asked, knowing that their team, led by Kurotsuchi Mayuri, were the health technology team.
“In all other cases, yes, but they turned down this project.” Hiyori huffed, entering the empty meeting room. “They said some bullshit about other projects of theirs being of higher priority.”
Well, that’s fair you thought, but Hiyori’s face looked like she didn’t buy it. “From the look on your face, you don’t think it’s true.” You laughed as she clenched her notebook.
“It’s because they don’t want to work with the consultant tied to the project.” Hiyori explained, her scowl growing deeper. “Not like I want him to work with you either.”
“I’ve worked with frustrating consultants in the past, Sarugaki-san.”
“I know, I know” Hiyori sighed, looking dejectedly at the window. “This guy’s annoying, and frankly, just plain weird.” She admitted. “I worked with him for a short while, he wasn’t completely a bad guy then. He just gets on my nerves.” She explained, honestly.
“Well, if you were able to tolerate him, then it should be fine.” You said, wondering what type of person would not only upset Hiyori (who was already quick to anger) and Kurotsuchi-san (who was already easy to annoy). You figured this person must have been normal to some degree, since the two people who have worked with him were a bit odd in their own ways.
Your manager explained in more detail the work you’d be doing and the finer technical details of the expectations senior management had for you. “The consultant is an expert in this field, which is why he’ll be assisting you on this. Apparently, he used to work for the national health board way back when.” Hiyori explained, as you diligently took notes.
“Anyways, that’s about it. I sent him a meeting invite to this board room in 5 minutes. I’ll email you everything we shared for your records. I gotta bounce, but send me a message if anything comes up.” Hiyori waved you goodbye as you sat alone in the room.
You checked your phone, scrolling through your calendar for the week. You were relatively social at work, with colleagues sending you invites to things to see, do and eat. You didn’t see the harm in participating, and you weren’t much for drinking to begin with, so you made sure your colleagues got home safe. Either way, you were appreciative of them inviting you out.
Five minutes turned to ten, and still no show of this infamous consultant.
You continued scrolling through your phone, going through your social media accounts. Acquaintances from school and previous jobs, were sharing engagements, wedding photos and many other milestones. You couldn’t help but smile sadly, with cold, belittling words ringing through your head.
This stuff isn’t meant for me anyways. You thought, as you continued to scroll through your feed.
It wasn’t until you saw the time, that almost half an hour had passed. You began to type a message to Hiyori about the no-show consultant, until he barged through the door.
Pale, disheveled blonde hair, and what you assume a white button down and a poorly tied dark green tie around his neck under a brown sweater, paired with dark grey slacks.
He immediately grabbed your hand and gave you an intense handshake. The suddenness threw you off and confusion was evident across your face.
“Ah, sorry about that! I’m Urahara Kisuke the technology consultant, and I suppose you’re the analyst I’m working with?” Urahara-san asked.
You nodded your head, while you flexed your poor hand that was caught off guard by his tight handshake. You introduced yourself and offered him a seat next to you. The two of you went over the technical details and scheduled to meet again tomorrow before your lunch break. Your phone began to buzz as your coworkers and friends began to barrage you with texts.
“My my, you really are popular.” Urahara teased, as he stared at your phone with curious eyes.
You couldn’t help but feel embarrassed from his comment, “no, not really” you explained, “I agreed to karaoke tonight, that’s all!”
Urahara gave you a soft smile, “that must be nice. Karaoke sounds wonderful. Have a great time.” You thanked him for his time today and rushed off to your coworkers.
He wasn’t so bad. You thought, as your coworkers waved at you near the elevators. You told them to wait for you in the lobby as you grabbed your belongings, unaware that Urahara was watching you from the hallway.

The karaoke bar was lively. Drinks were ordered, snacks were shared and laughter erupting from your private booth. You smiled at your friends who sung along badly to old pop hits, and laughed as they sang dramatic renditions of tearful ballads. You sang along, clapping with them, until you felt a gentle tap on your shoulder.
“I heard you met Urahara Kisuke today.” Rukia quietly whispered.
You stopped clapping and turned to face her as the rest of the room kept singing along.
“Oh yes I did Kuchiki-san! He was quite polite and knowledgeable. He really knows his stuff.”
Rukia gave you a puzzled expression, “really? I heard he’s kind of shady.”
“It’s funny you say that, my manager said that as well, and she mentioned Kurotsuchi-san saying something similar.” Rukia’s face turned to one of concern, “but I’m going to be meeting with him for the rest of the month, so I’ll tell you if anything interesting comes up.” You laughed, trying to lighten the mood.
“Ok, but just be careful. I heard from Rangiku at Payroll that they weren’t able to fire him because he has deep connections to some of the executives.”
That surprised you. The company itself was old, nearing 50 years (or so they say). You didn’t know much about Urahara Kisuke as his field of work was different from yours. You made a mental note to look into him later tonight. “What was it that made them consider firing him?” You were curious to know why everyone you’ve spoken to about him, had such poor opinions of the man.
“I’m not sure, I heard he was doing insider trading?”
“Really!?” You exclaimed, “wouldn’t the cops be involved then?” Pointing out the discrepancy within the rumour.
“Oh… yeah..” Rukia was stumped, “I’ll ask Rangiku next time I see her then. Maybe she doesn’t know either.”
“Or maybe it’s just a baseless rumour?”
Rukia gave you a look of uncertainty, “just be careful around him, ok? Rumours start from somewhere you know…”
You laughed her comment off and treated her to favourite snack. You were left with an uncomfortable feeling the rest of the night and excused yourself to leave early.
At home, you looked into Urahara Kisuke. Several of his papers came up, all of them focused on some aspect of biomedical engineering. You saw a Kurotsuchi-san’s name come up frequently as a collaborating author, and another person, “Aizen Sosuke” come up. You ran a quick search on him and saw he was working as a professor in the top university in the country. Nothing else came up in your search though, which left you more questions than answers.
You always tried to give everyone the benefit of the doubt, and Urahara-san was no different, maybe it’s just a baseless rumour after all. Whatever the case may be, work was work, and you resigned yourself to be professional and complete the project to the best of your abilities.
You had meal prepped your lunch for tomorrow then prepared for bed. You still couldn’t shake off everyone’s comments today, so you hoped sleep would wash the thoughts away.

It had been several weeks now of meeting with Urahara-san. Your time with him made you doubt the comments made by your colleagues and friends when you first started the project. Now it was nearing the end of it, and if anything, if someone were to ask you to describe “Urahara Kisuke”, you would say he was a “curious, yet brilliant man who tries to be funny.” You laughed at yourself when you remembered the terrible “jokes” Urahara-san made, but he was certainly an interesting person.
Today was your last meeting with him though, and a small part of you was sad. You liked spending time with him. You watched him skim your report on the laptop screen with an intense focus, typing in tracked changes sparsely in between.
“I’m impressed!” Urahara said to you, “you really nailed this review. I know the execs will love it.”
You smiled at his compliment, “I’m flattered, Urahara-san, but it’s your vast knowledge that really helped me. I wouldn’t have even known to look in the formulary database and disability policies!” You said, shaking your head.
“They really are right about you.” Urahara remarked in a serious tone.
You looked at him with curiosity.
Urahara chuckled and in a teasing tone, “that you’re incredibly studious and hardworking! I barely did anything.”
“Well I have to say people are wrong about you.” You beamed at him, “people were telling me all sorts of rumours about you, and to be cautious.”
Urahara raised his eyebrows, but let you continue on.
“But you’re actually quite friendly and diligent.” You give an awkward laugh, “and I’ll miss working with you.”
Urahara looked surprised. He had never heard that before. Most people found him, in some ways, too difficult to work with. His unorthodox approach to analyzing and finding results, and dubious ethics, made finding people to work with slim to none. Yet here you are.
They really are right about you. He thought to himself. It bothered him, to some degree. Initially he wondered what angle you would be playing at while working with him. Would you fish him for gossip? Would you be a bother and ask about his past research? An annoyance who wanted access to his connections, his work?
No, none of that came up. You approached him with sincerity and kindness, something he wasn’t dealt with in his years of working as a researcher.
“Urahara-san, if you have some time,” you ask, your face growing warm, “would you care to join me for lunch?” To say he was startled was an understatement, but he accepted.

“Is that all you’re going to eat, Urahara-san?” You ask, noticing his canned coffee and prepackaged rice ball.
“Oh this,” Urahara laughed, “I had a hearty breakfast, so I wanted a light lunch.” He lied to you, while wearing a large grin on his face.
“If you want, you can have some of my food.” You offered to him. “I don’t think that’ll last you through the afternoon.” You gave him a sheepish smile.
Urahara’s eyes widened, but he chuckled, waving you off. But you were full of surprises, you pushed forward your lunch to him, “why don’t you have some of mine?” Your face grew hot as you began to ramble, “I know I may not look it, but I’m a pretty decent cook.”
He was hesitant, but the earnest tone in your voice, and the way you avoided his eyes told him enough. He picked up the utensil and took some food for himself.
Urahara’s eyes widened but quickly shifted. “My, you certainly know your way around the kitchen!” He joked, a slight smile on his face as he noticed the way your eyes avoided him, but the pleased smile on your face.
It felt unusual to him, to enjoy someone’s company like this, it put him on guard. He would listen to you talk, watch your reactions, and try to rationalize what you wanted out of him. But before he could make a definitive conclusion, your lunch break was over.
“Thank you for spending your lunch break with me, Urahara-san.” You said softly, “if you’re free the rest of the week, I’d like to do this again.”
His mind raced, maybe you were interested in something more personal from him, his under-the-table work, maybe you were sent by Kurotsuchi or the higher ups to investigate him.
But a small part of his brain knew that wasn’t right, he’d have to get to the bottom of this. “Yes, I’d love that.” He gave you a smile.

Two weeks had gone by where, for the most part, you and Urahara had lunch together at work. You were dismayed by his lack of lunches some days. He would say he was too busy to prepare something, or having a larger breakfast made his appetite quite small. But you had your suspicions.
“Urahara-san, what’s your favourite meal to cook?”
Urahara made an exaggerated sigh and cupped his chin, “why lately, it’s been what you’ve shared with me at lunch.”
You couldn’t help but laugh, “I’m serious! I’d love to know what you make. I want to try new recipes.” You gave him a sincere smile.
It’s what bothered Urahara about you, you were too sincere, too earnest with someone like him. He suspected you didn’t know the actual rumours surrounding him, and a part of him hopes you never do. His heart, much to his dismay, would flutter seeing you smile, seeing your eyes light up. He would watch, as he wandered around the company’s different units, how you interacted with other coworkers and colleagues. You were polite and friendly. So… disarming.
Urahara let out a sigh, it would be so easy to let you go if you were only spending time with him for nefarious reasons. He wouldn’t have had any qualms about leaving you high and dry. But even on the weekends, he would send you a short text, something about how your weekend was going.
A small part of him was growing jealous at how you would hang out with some of your coworkers after work. Your social circle seemed so large compared to him… but he wanted to be at the centre.
“I don’t have one. I can’t say I’ve cooked much for myself.” Urahara murmured, scratching his head.
You looked at him with shocked eyes, “no way! Not even scrambled eggs?”
Urahara let out a laugh, “ok, maybe one.” He looked at your now empty bento that he had nibbled on, “if you have the time…”
You looked at him with such an eager expression, the knot in his stomach tightened, as he tried to ignore the thudding of his heart. He wouldn’t act on feelings; this was a plan to let you slip up what your real reasons were to spend time with him.
“Would you teach me how to cook?”
And as he suspected as much, and denying his own relief from your words, you agreed. “Why don’t you pick a recipe you want to try and you can come over to my house on Sunday?”
“Sure,” Urahara said, his brain already laying down plans to ensnare you, “but won’t your boyfriend mind if I come over?” He asked, with a hesitant look on his face.
“If I did have one, maybe!” You laughed, “You don’t have to worry about that, trust me.” You looked away from him, a sad look on your face. Urahara narrowed his eyes, but before he could ask more, your smile was back, “just let me know what ingredients to buy.”
“Don’t worry about that.” Urahara said, “I’ll bring the ingredients. It’s the least I can do since you’re offering your kitchen.”
“Oh alright! Thank you for going through the trouble.” You smiled, “let me know how much it is and we can split the bill.” Urahara laughed at your comment, you really were so honest.
“No, it’s on me. Especially after feeding me lunch these past few weeks.”
You let an awkward laugh, before avoiding his gaze. “My only request is that,” Urahara lowered his voice, bring his face close to yours, “don’t invite anyone else – I want your undivided attention.”


THANKS FOR READING MY FIRST CHAPTER!!
I've already have drafted over 5 chapters for this story and I have an ending in mind for it too. As a personal goal, I want to complete this, so I hope you join me along for this ride!
#bleach#urahara kisuke#urahara kisuke x reader#urahara kisuke x you#bleach urahara#bleach x you#bleach x reader#bleach x y/n#urahara x reader#kisuke bleach
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
Our body's circadian clock affects everything from sleepiness to metabolism – and it might also influence how effective certain cancer treatments are, according to recent research. Checkpoint inhibitors are immunotherapy drugs that block crucial proteins from binding to cancerous tumors, meaning the immune system's T cells can more easily recognize and kill the cancer off. They are a good idea in theory, especially as the drugs are less toxic than chemotherapy, but scientists are trying to find ways to increase the impact of this approach in practice. In the US, several checkpoint inhibitor therapies are currently approved for human use, but while these drugs can treat a wide variety of cancers, they only work for some patients.
Continue Reading.
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
#Metastatic melanoma#checkpoint blockade#immunotherapy#surgery#oligometastatic disease#tumor resection#immune checkpoint inhibitors#anti-PD-1#anti-CTLA-4#systemic therapies#symptom palliation#diagnostic biopsy#staging procedures#multidisciplinary approach#tumor shrinkage#surgical timing#cancer treatment#melanoma management#oncologic outcomes#precision oncology.#Youtube
0 notes
Text

Inspiring Cancer Therapy
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, therapies which prevent cancers circumventing attack from the immune system, often fail because they don't activate the patient's immune system sufficiently. This study finds that mice with lung cancer muster an enduring immune response when such therapy is delivered as a nanoemulsion by nebuliser
Read the published research article here
Image from work by Rong A, Zhaoguo Han, Meifang Zhou and Chaoqun Nie and colleagues
Department of Nuclear Medicine, The Fourth Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)
Published in Science Advances, November 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Global CTLA-4 Therapies Market - Unveiling Cutting-Edge Insights
Global CTLA-4 Therapies Market
The global CTLA-4 Therapies market is expected to reach USD 1384.4 million by 2030, at a CAGR of 7.1% during the forecast period 2022 to 2030. The modulation of cell motility and/or PI3 kinase signaling may also be other ways that CTLA-4 works. Early multiphoton microscopy investigations to observe T-cell movement in healthy lymph nodes seemed to support the "reverse-stop signalling paradigm."
Click here for full report:
https://www.pharmanucleus.com/reports/ctla-4-therapies
Market Overview
The protein receptor CTLA-4, also known as CD152 (cluster of differentiation 152) or CTLA4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4), serves as an immunological checkpoint and suppresses immune responses. A characteristic that is especially noticeable in malignancies is the constitutive expression of CTLA-4 in regulatory T cells as opposed to the upregulation of this protein in conventional T cells following activation. When attached to CD80 or CD86 on the surface of antigen-presenting cells, it functions as an "off" switch. An inhibitory signal is sent to T cells by the immunoglobulin superfamily member CTLA-4, which is produced by activated T cells. Similar to the T-cell co-stimulatory protein CD28, CTLA-4 binds to antigen-presenting cells' CD80 and CD86, also known as B7-1 and B7-2, respectively. CTLA-4 outcompetes CD28 for its ligands because it binds CD80 and CD86 with greater avidity and affinities. T cells receive an inhibitory signal from CTLA-4 while receiving a stimulatory signal from CD28. Additionally present in regulatory T cells (Tregs), CTLA-4 is a component of their inhibitory activity. CTLA-4 expression is enhanced by T cell activation via the T cell receptor and CD28. It's still unclear how CTLA-4 affects T cells and how it does so. According to biochemical data, CTLA-4 attenuates the signal by bringing a phosphatase to the T cell receptor (TCR). Since this work was first published, it has not been supported by the literature. Recent research has revealed that CTLA-4 may work in vivo by engulfing and removing CD80 and CD86 from antigen-presenting cells' membranes, rendering them inactive for CD28 triggering.
Click here for full report:
https://www.pharmanucleus.com/reports/ctla-4-therapies
Market Dynamics
T-cell immunological activity is negatively regulated by immune checkpoints called programmed death 1 (PD-1) and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4). New immunotherapies for melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and other cancers have been developed as a result of the inhibition of these targets, which boosted immune system activation. Ipilimumab, a CTLA-4 inhibitor, is approved to treat advanced or incurable melanoma. In patients with metastatic or incurable BRAF WT melanoma, the combination of ipilimumab and nivolumab has also been authorized. Inhibiting immune responses, especially anticancer responses, play unique roles for CTLA-4.
Mutations in the CTLA4 gene, which provides instructions to cells for producing the CTLA4 protein, are the cause of CTLA4 deficiency. The immune system's activity is slowed and controlled by this protein, which acts as a brake. The CTLA4 gene is two copies per person, one from each parent. In 2014, researchers from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) discovered that individuals with only one functional copy of CTLA4 have abnormal T-cell activity, lower levels of normal, antibody-producing B cells, higher levels of autoimmune B cells, and disruption of organs by invading immune cells. The scientists came to the conclusion that a single functional copy of CTLA4 is insufficient to generate enough CTLA4 protein for a healthy immune system.
Request for free sample report”
https://www.pharmanucleus.com/request-sample/1178
While PD-1 suppresses T cells later in an immune response, largely in peripheral tissues, CTLA-4 is hypothesized to control T-cell proliferation early in the immunological response, primarily in lymph nodes. Due to the molecular distinctions between these 2 checkpoints, immuno-oncology drugs that block them may have different clinical characteristics.
Intestinal sickness, respiratory infections, autoimmune issues, swollen lymph nodes, the liver, and the spleen are just a few of the symptoms caused by the rare ailment CTLA4 deficiency, which significantly inhibits the immune system's ability to regulate itself. In 2014, NIAID researchers and their associates discovered the illness.
Segmentation Analysis:
Based on the treatment, the CTLA-4 therapies market is categorized into autoimmune conditions and immunoglobulin deficits, and others. In 2022, the autoimmune conditions and immunoglobulin deficits segment accounted for the largest share of the market, with 59% and a market revenue of 472 million. Standard treatments for autoimmune conditions and immunoglobulin deficits may be used to treat CTLA4 deficiency. The medicine CTLA-4-Ig, also known as abatacept, which mimics the action of the CTLA4 protein and lowers immunological activity, is a potential new treatment. Abatacept is used to treat autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, but more research is needed to determine whether it is also beneficial in treating CTLA4 deficiency. Researchers from the NIAID began a small clinical trial in 2019 to examine the efficacy and safety of intravenous infusions of abatacept for restoring or enhancing blood cell counts in persons with CTLA4 deficiency. The medication abatacept, which Bristol-Myers Squibb produces, is being given to the research.
Based on the end-user, the CTLA-4 therapies market is categorized into?clinical & laboratories, hospitals, and others. In 2022, the clinics & laboratories segment accounted for the largest share of the market, with 40.1% and a market revenue of 320.8? million. The immune dysregulation syndrome that includes substantial T cell infiltration in a number of organs, including the gut, lungs, bone marrow, central nervous system, and kidneys, is present in symptomatic CTLA-4 mutant patients. Most patients suffer from enteropathy or diarrhea. Autoimmunity, lymphadenopathy, and hepatosplenomegaly are also frequent. Thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, thyroiditis, type I diabetes, psoriasis, and arthritis are among the various organs that are impacted by autoimmunity. Additionally prevalent are respiratory illnesses. It's important to note that clinical manifestations and illness progression vary, with some people being severely impacted while others have minimal disease manifestation. Even within the same family, this "variable expressivity" can be noticeable and may be explained by variations in lifestyle, exposure to pathogens, treatment effectiveness, or additional genetic modifiers.
Regional Segment Analysis of the CTLA-4 Therapies Market
Asia Pacific emerged as the largest market for the global CTLA-4 Therapies market, with a market share of around 39% and 800 million of the market revenue in 2022.
Competitive Landscape
The report offers the appropriate analysis of the key organizations/companies involved within the global CTLA-4 Therapies market along with a comparative evaluation primarily based on their product offering, business overviews, geographic presence, enterprise strategies, segment market share, and SWOT analysis. The report also provides an elaborative analysis focusing on the companies' current news and developments, including product development, innovations, joint ventures, partnerships, mergers & acquisitions, strategic alliances, and others. This allows for the evaluation of the overall competition within the mark
#CTLA-4 Therapies Market#Global Market Trends#Latest Therapeutic Advancements#Innovations in CTLA-4 Therapies#Recent Developments in Immunotherapy#Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors#Cancer Treatment Breakthroughs
0 notes
Text
Bradford Hill evidence for causation - 33 plausible mechanisms and case reports
Ignore Science
Nov 04, 2024
Dr. James Royle is a practicing general and colorectal surgeon and he is warning about the high likelihood of causal relationship between the contaminated convid genetic technology injections and rapidly progressing cancers as evidenced by the gold standard Bradford Hill epidemiological criteria. sourceSubscribe
I will expand on these criteria and elucidate many more plausible mechanisms. But first here are more experts telling you the truth. Turbo cancer is not a formal medical diagnosis. It is widely used in the vernacular to describe rapidly accelerating cancer. Here is Dr. Paul Marik one of the most published critical care physician in the world:
The technical medical diagnosis is hyperprogressive disease (HPD) and it is well acknowledged in the medical literature especially in the context of immunotherapy drugs like immune checkpoint inhibitors which remove any suppression of the T cell response.
Oncologist Dr. William Makis explains and provides many biological mechanisms including the trojan horse lipid nanoparticle and immune system damage: source
I am including this medical reference to verify my claim the correct medical term is hyperprogressive disease (HPD). It is also illuminating as the proposed mechanisms for HPD overlaps with the injection namely anti-programmed death/ligand-1 monoclonal antibodies. source
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://joyrulez.com/blogs/430025/Immune-Checkpoint-Inhibitors-Market-Size-Overview-Share-and-Forecast-2031
The Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market in 2023 is US$ 47.22 billion, and is expected to reach US$ 158.26 billion by 2031 at a CAGR of 16.32%.
#Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market#Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market Analysis#Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Market Trends
0 notes
Text
The Power of Immunotherapy: A Deep Dive into Cancer Treatment
Immunotherapy, a groundbreaking approach in cancer treatment, has been making waves in the medical world. 🌟 But what exactly is it, and how does it work? Let's delve into the intricacies of this cutting-edge therapy. 💉
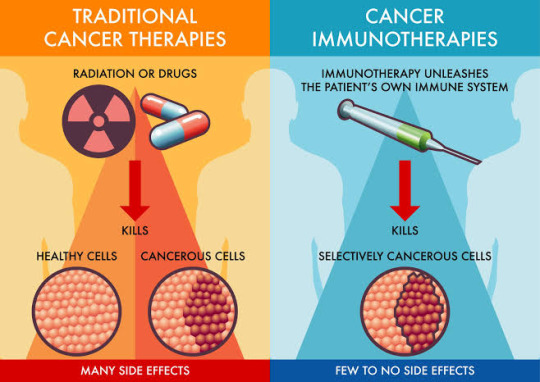
Immunotherapy at a Glance: 🔬 Immunotherapy, or immuno-oncology, is a therapeutic strategy that harnesses the body's immune system to combat cancer cells. Unlike traditional treatments like chemotherapy, which target both healthy and cancerous cells, immunotherapy is highly targeted, making it a game-changer in the fight against cancer.
Key Players in Immunotherapy: 🦠
Tumor Antigens are molecules found on cancer cells that act as red flags, signaling the immune system to attack. 👥
T Cells: The immune system's soldiers. They are trained to recognize and destroy threats, including cancer cells.
💡 Checkpoint Inhibitors: Proteins that, when blocked, enhance the immune response against cancer. 🧬
CAR-T Cell Therapy: Genetic engineering to supercharge T cells for precision attacks on tumors.
How Does Immunotherapy Work? Immunotherapy comes in various forms, but they all aim to accomplish one goal: boost the immune system's ability to recognize and eradicate cancer cells. Whether through checkpoint inhibitors, vaccines, or CAR-T cell therapy, the goal remains: empower the immune system's fighters!
Immunotherapy is a testament to the power of science and innovation, offering new hope to cancer patients worldwide. 🌍
Let's continue to explore, research, and advance this remarkable field to improve the lives of those affected by cancer.
References:
Postow, M. A., Callahan, M. K., & Wolchok, J. D. (2015). Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 33(17), 1974–1982. doi:10.1200/jco.2014.59.4358
Rosenberg, S. A., Yang, J. C., & Restifo, N. P. (2004). Cancer immunotherapy: moving beyond current vaccines. Nature Medicine, 10(9), 909–915. doi:10.1038/nm1100
June, C. H., & Sadelain, M. (2018). Chimeric Antigen Receptor Therapy. New England Journal of Medicine, 379(1), 64–73. doi:10.1056/nejmra1706164
#immunotherapy#science#biology#college#education#school#student#medicine#doctors#health#healthcare#immune system#cancer#disease#immune health#immune response
58 notes
·
View notes